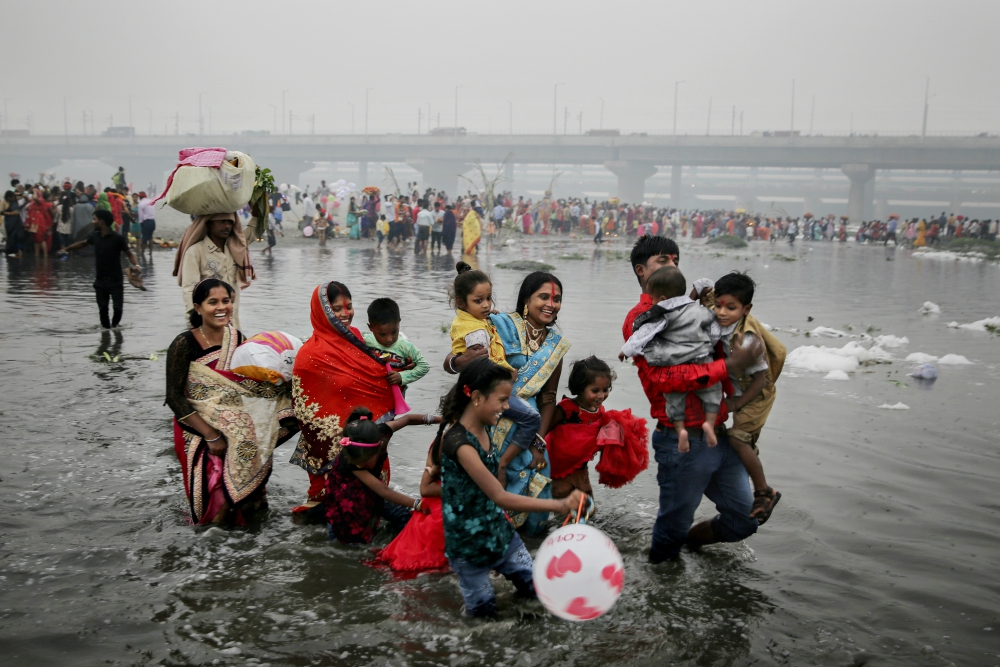
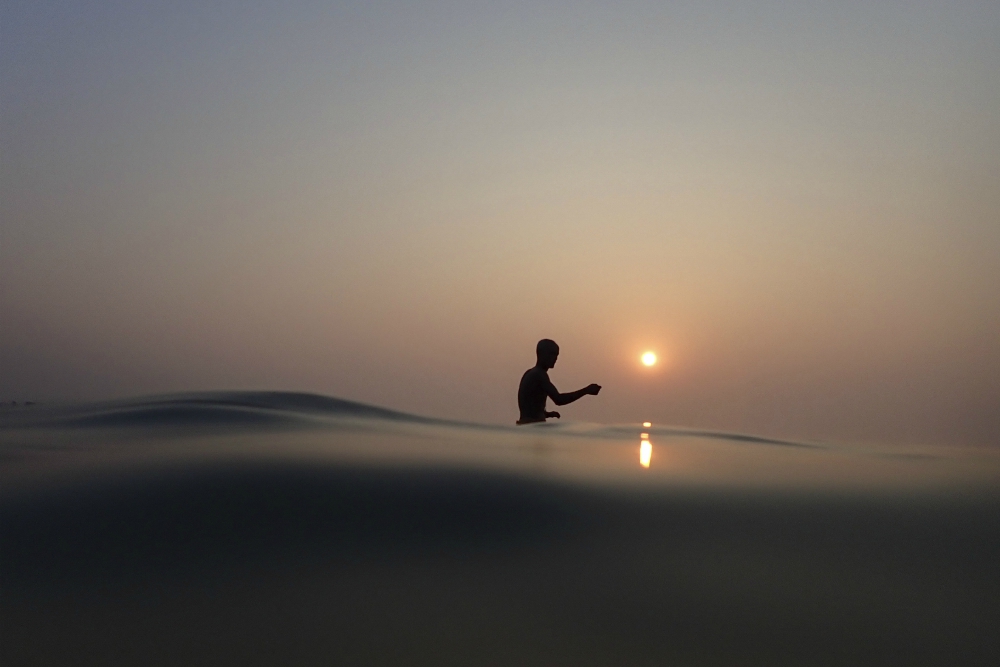
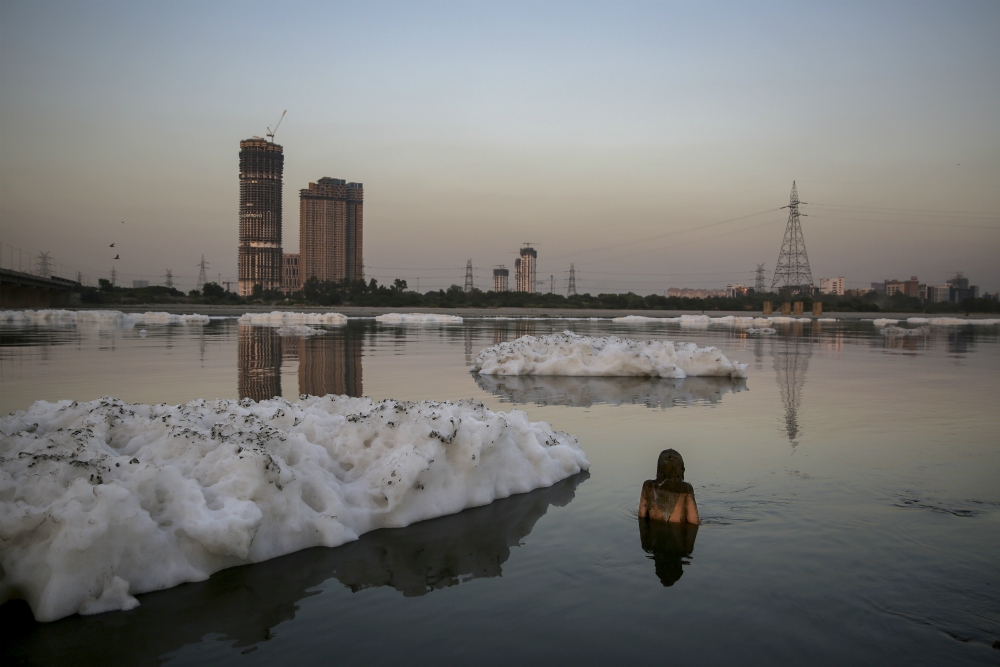
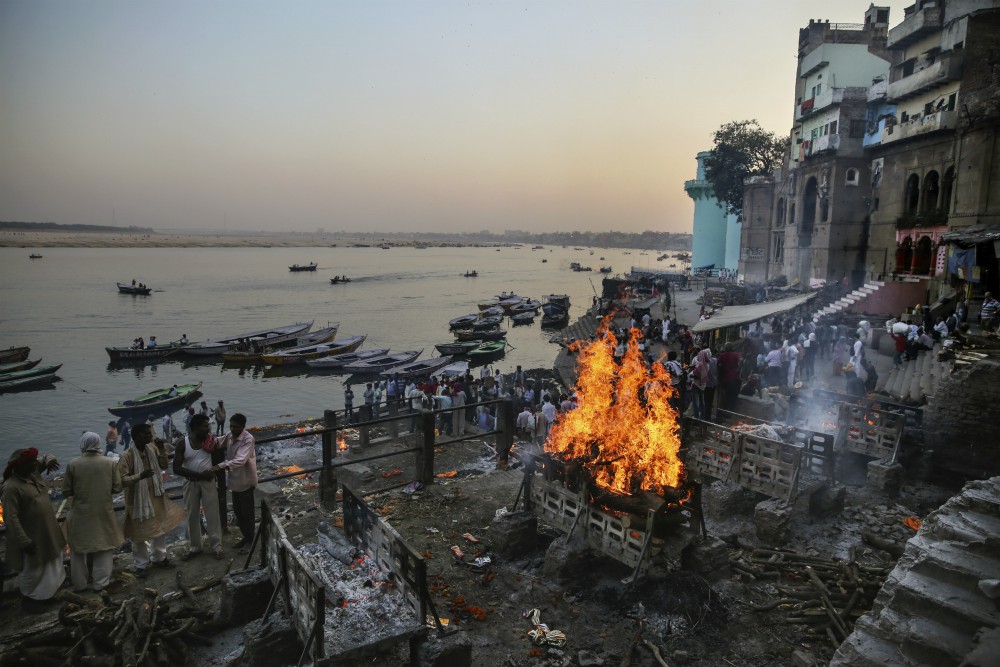An Indian Hindu family walks on the shallow banks of the Yamuna river, covered with chemical foam caused by industrial and domestic pollution, during Chhath Puja festival in New Delhi on Nov. 2, 2019. Despite the river being accorded the status of a living human entity by an Indian court, untreated sewage and industrial pollutants have turned it into one of the most polluted rivers in the world. The Yamuna is one of the major tributaries of the Ganges. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
More than 2,000 years ago, a powerful king built a fort on the banks of India's holiest river, on the fringes of what is now a vast industrial city.
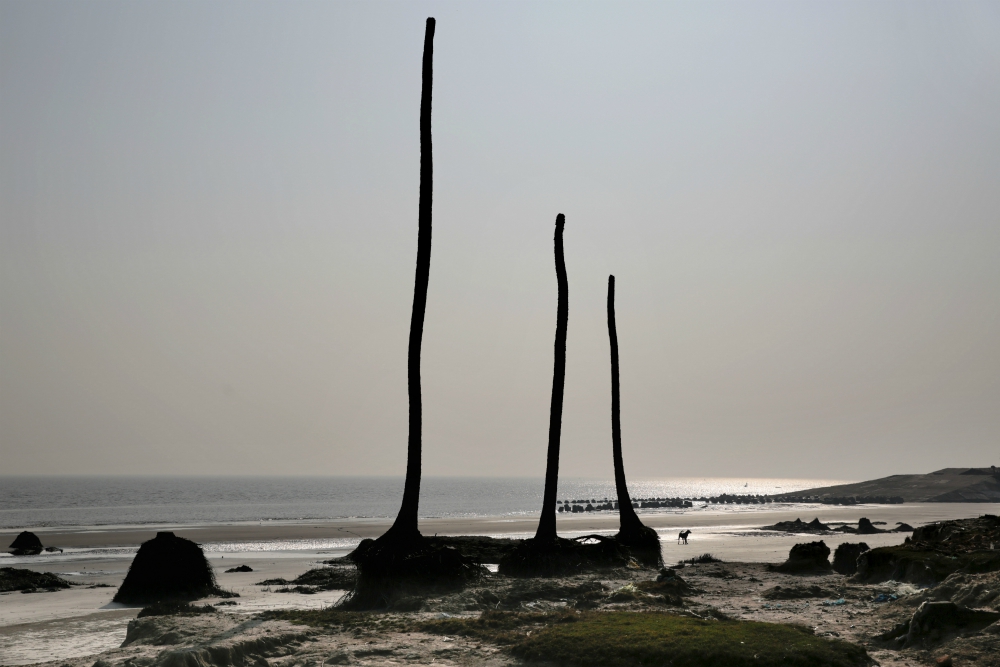
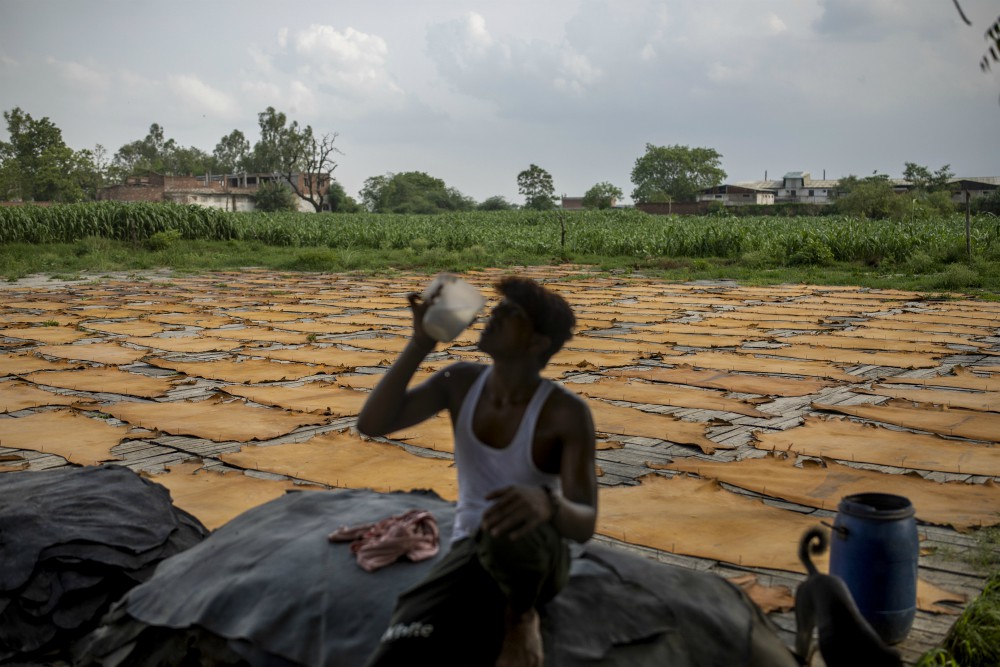
Today, little of the ancient construction remains, except for mounds of rubble that tannery workers pick through for bricks to build shanties atop what was once the fortress of the great King Yayati.
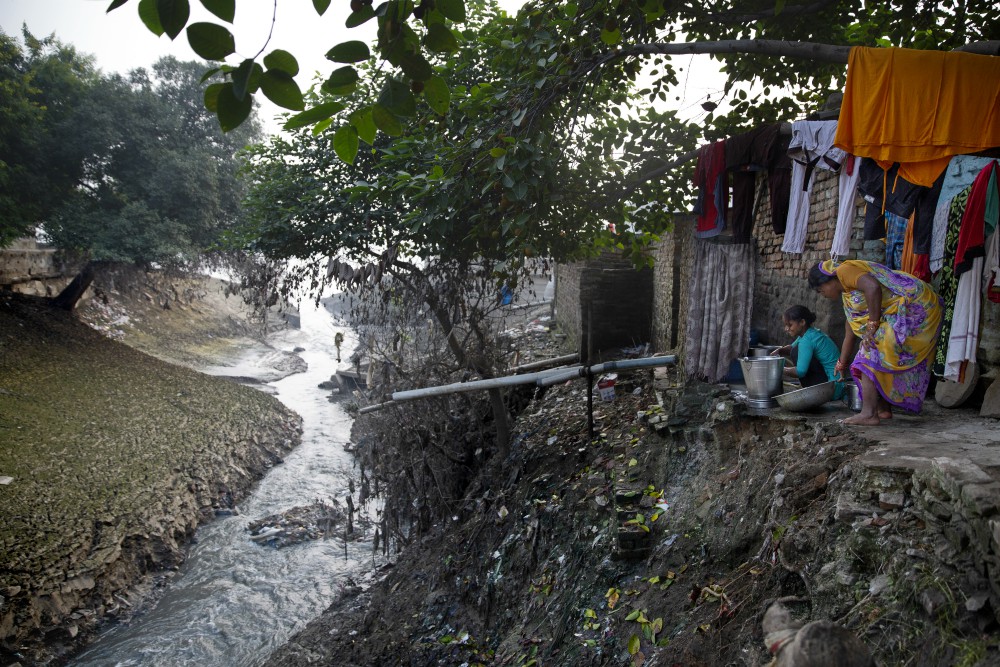
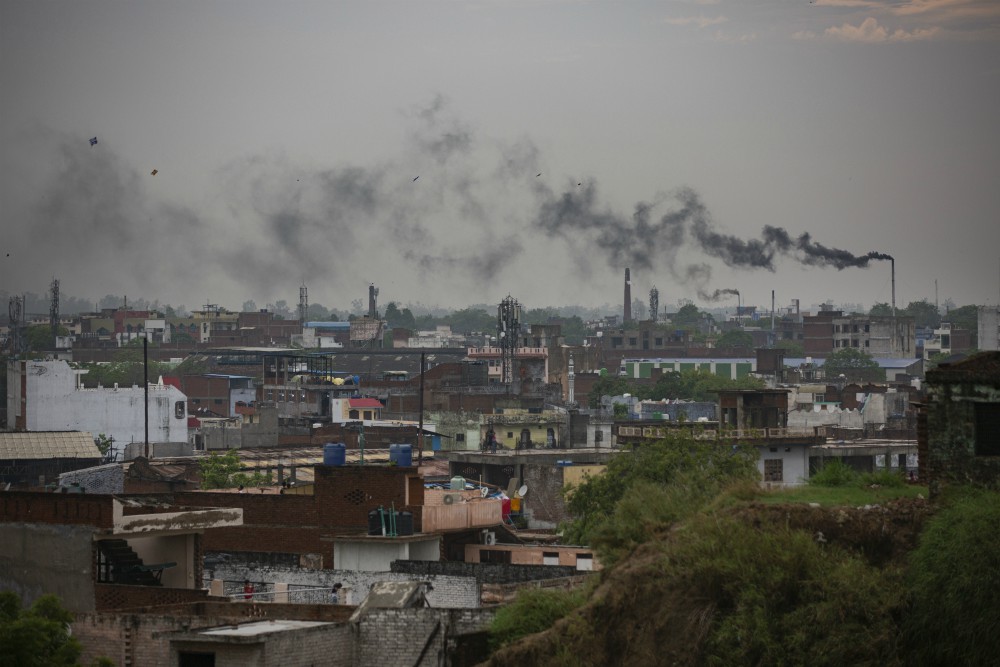
And Kanpur, where Yayati built his fort, is a city known for its leather tanneries and the relentless pollution they pump into the Ganges River.
For more than 1,700 miles, from the Gangotri Glacier in the Himalayas to the Bay of Bengal, the Ganges flows across the plains like a timeline of India's past, nourishing an extraordinary wealth of life. It has seen empires rise and fall. It has seen too many wars, countless kings, British colonials, independence and the rise of Hindu nationalism as a political movement.
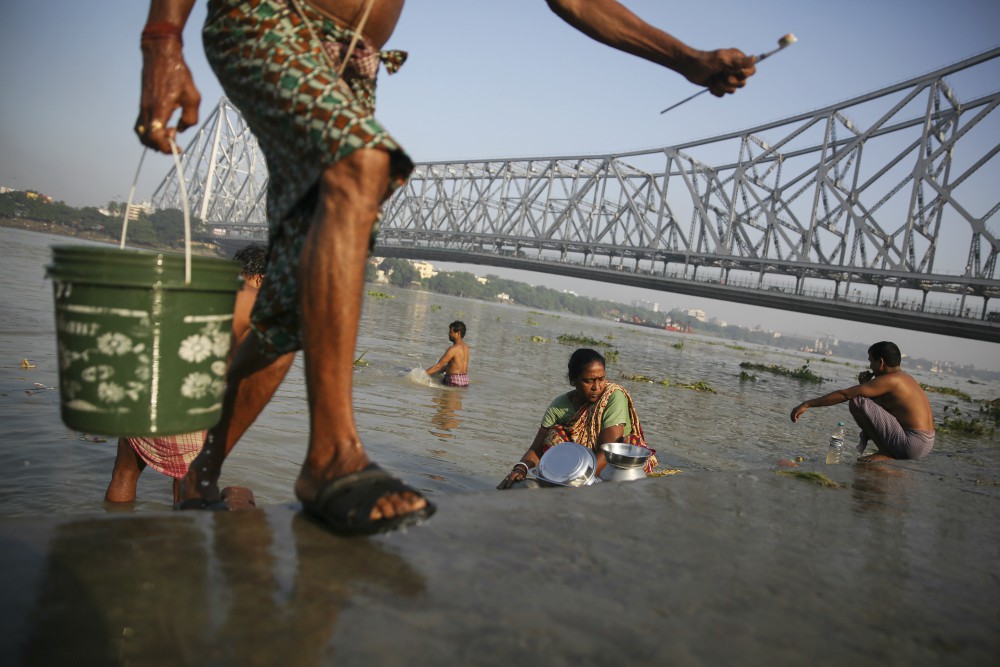
In India, the Ganges is far more than just a river. It is religion, industry, farming and politics. It is a source of water for millions of people, and an immense septic system that endures millions of gallons of raw sewage.
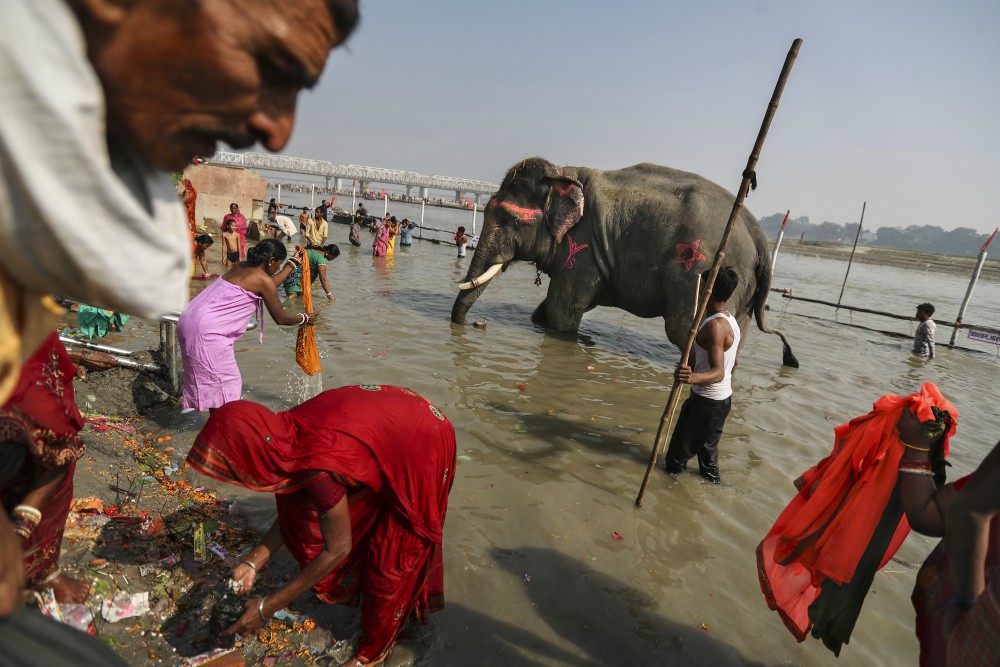
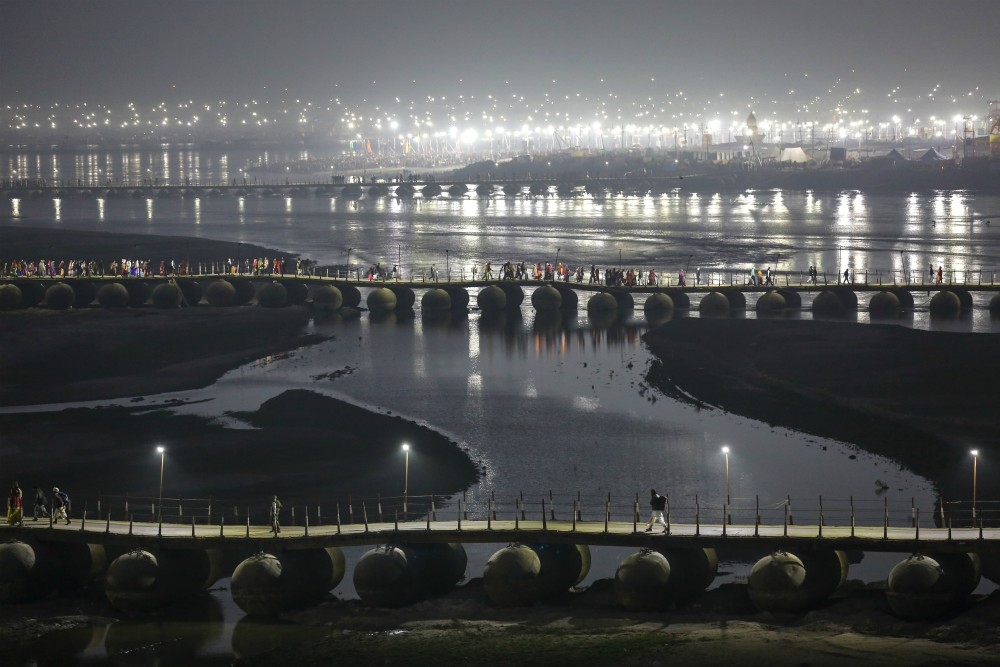
To Hindus, the Ganges is "Ganga Ma" — Mother Ganges — and a center of spiritual life for more than a billion people. Every year, millions of Hindus make pilgrimages to the temples and shrines along its shores. To drink from it is auspicious. For many Hindus, life is incomplete without bathing in it at least once in their lifetime, to wash away theirs sins.
But all is not well with the Ganges.
Pollution has left large sections of it dangerous to drink. Criminal gangs illegally mine sand from its banks to feed India's relentless appetite for concrete. Hydroelectric dams along the river's tributaries, needed to power India's growing economy, have infuriated some Hindus, who say the sanctity of the river has been compromised.
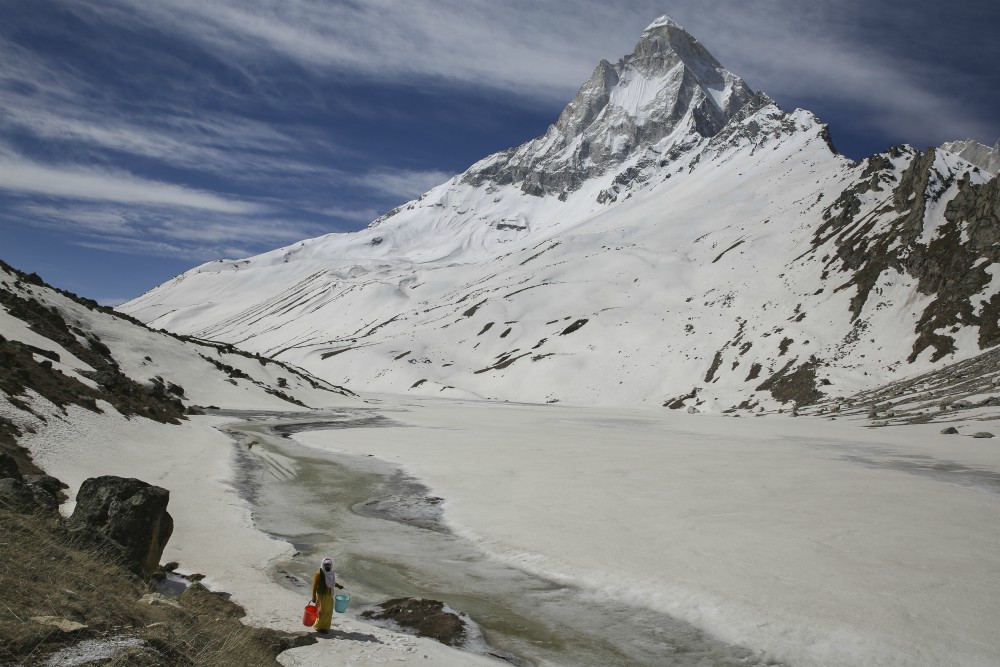
And over the past 40-some years, the Gangotri Glacier — source of almost half the Ganges' water — has been receding at an increasingly frightening pace, now losing about 22 meters per year.
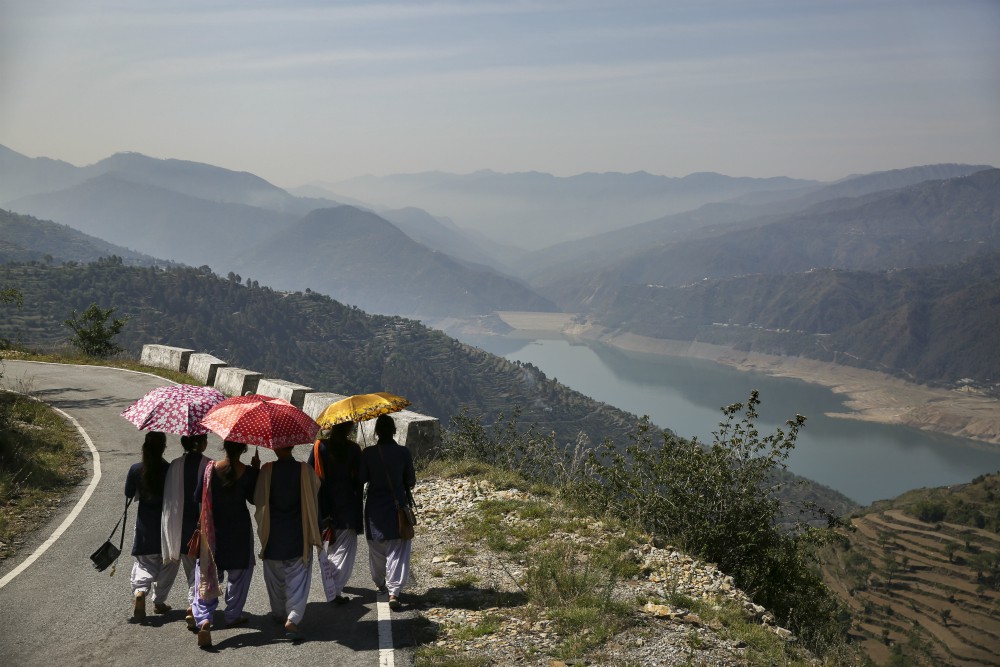
For millennia, the Gangotri's glacial melt has ensured the arid plains get enough water, even during the driest months. The rest comes from Himalayan tributaries that flow from the colossal chain of mountains.
As the Ganges flows across the plains, its once clean and mineral-rich water begins collecting the toxic waste from the millions of people who depend on it, becoming one of the most polluted rivers in the world. Millions of liters of sewage, along with heavy metals, agricultural pesticides, human bodies and animal carcasses, are dumped into the Ganges every day.
At times, officials try to fix things, but vast stretches of it remain dangerously unhealthy.
Still, to Hindus, the river remains religiously pure.
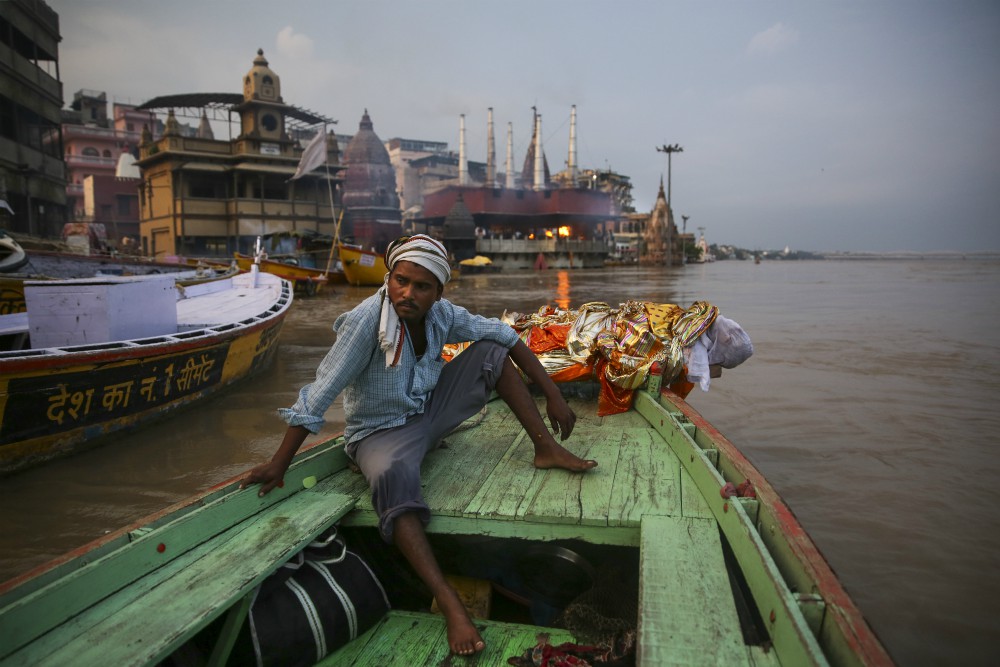
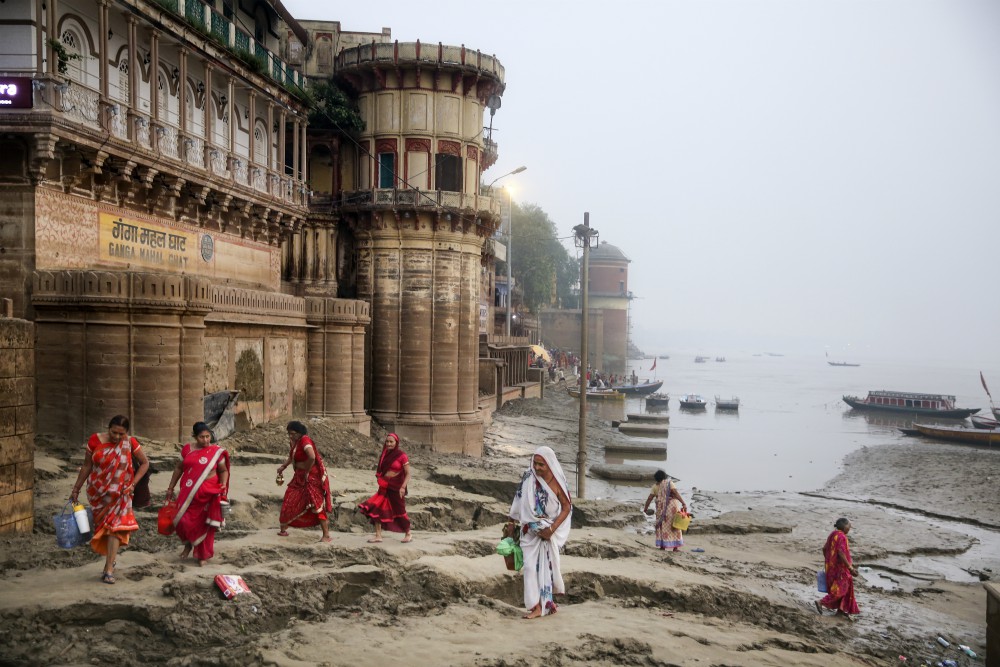
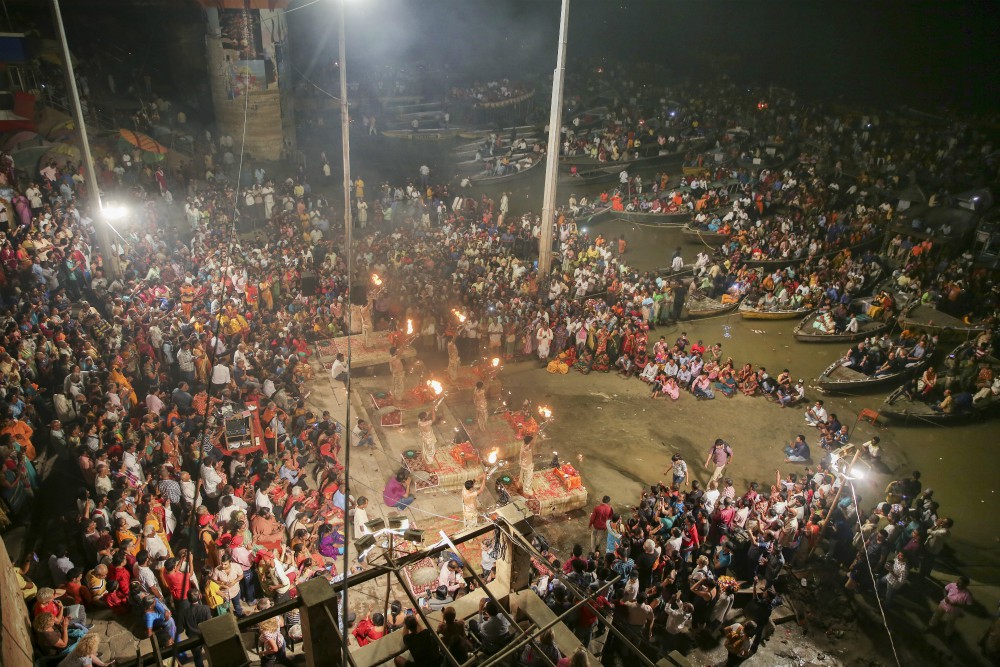
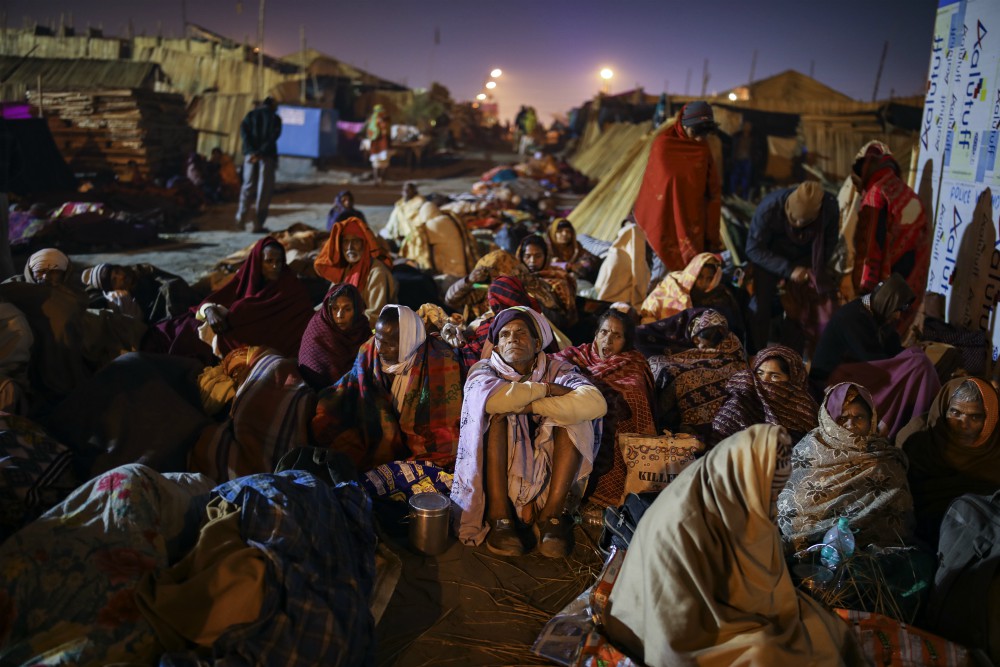
Every year, tens of thousands of Hindus bring the bodies of their loved ones to be cremated at the Ganges, in the city of Varanasi. A Hindu who dies in the city, or is cremated alongside it, is also freed from that cycle of birth and death.
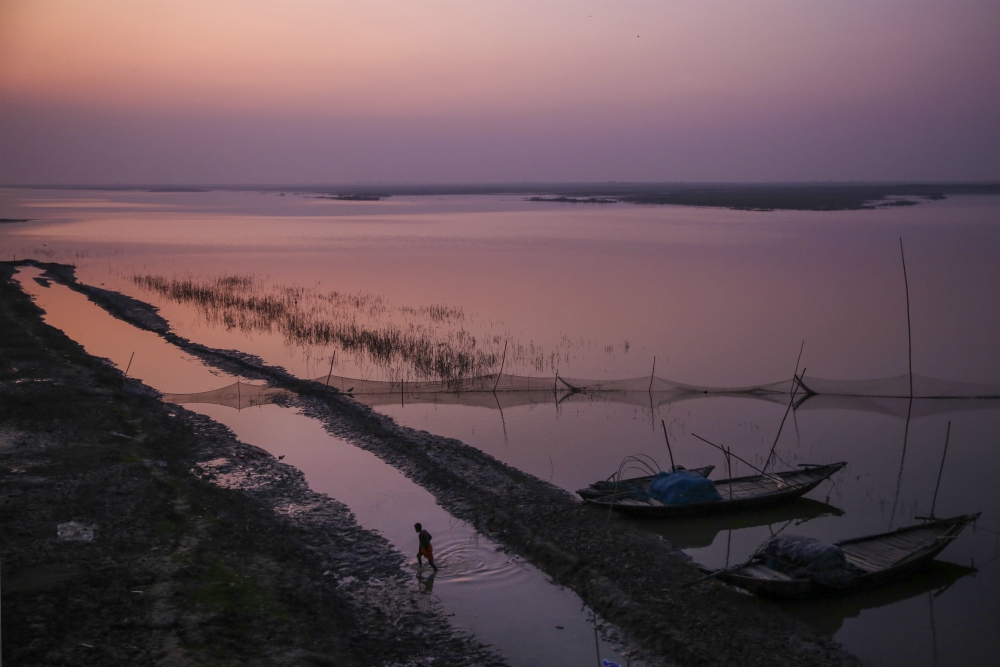
After Varanasi, the Ganges continues its eastward journey through endless farmland as it nears the coast, eventually splitting off into ever-smaller rivers in the great wilderness of her delta. The biggest river, the Hooghly, heads south toward the sea, passing through Kolkata, the largest city in eastern India. Once the capital of the British raj, known as Calcutta, today the metropolis is home to nearly 15 million people.
Eventually, its waters spill into the Bay of Bengal.
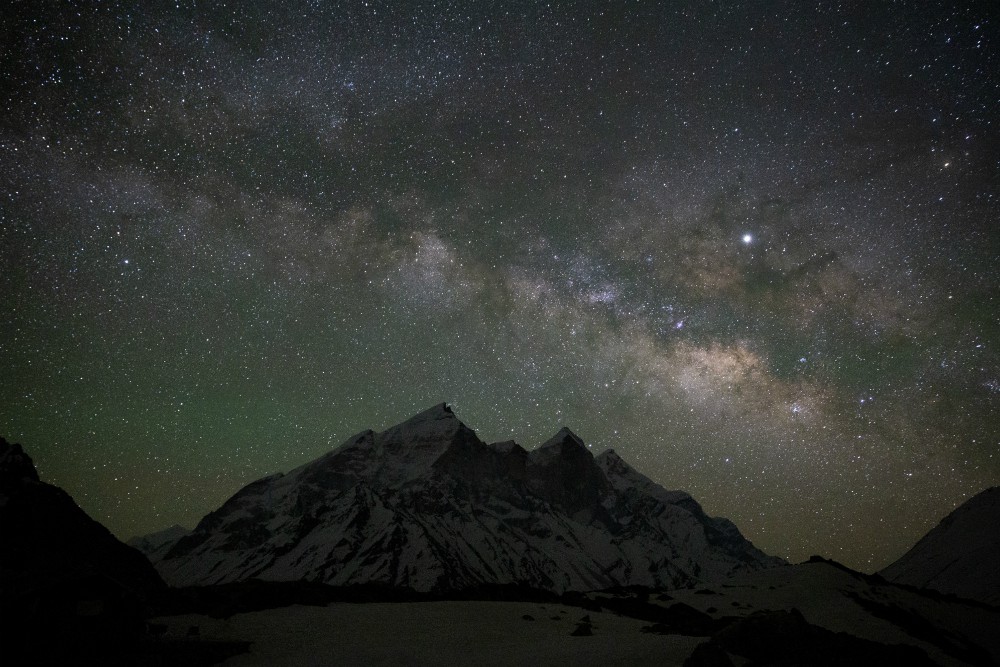
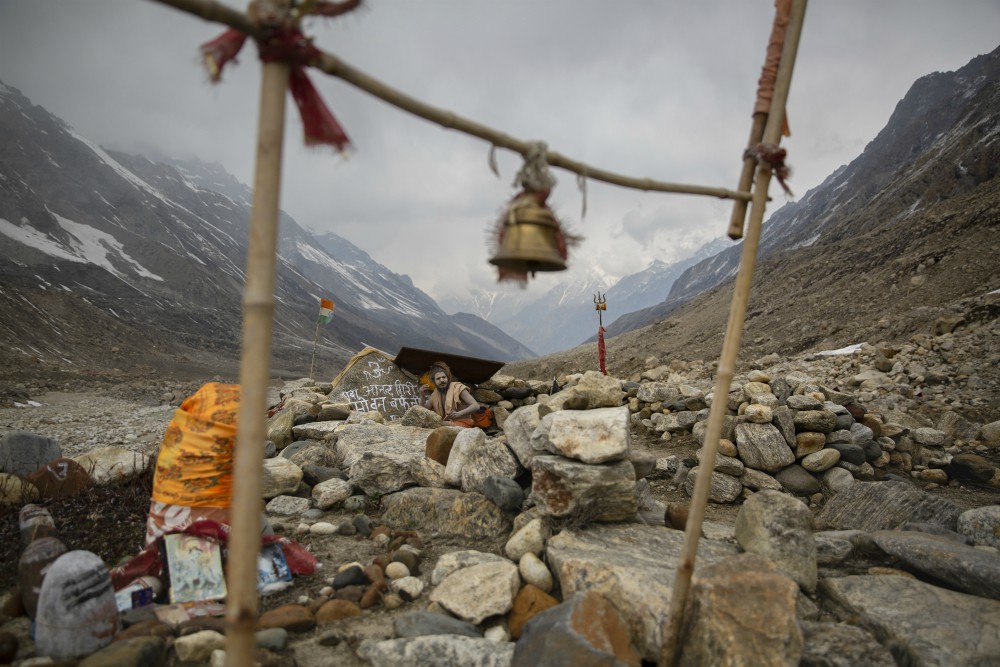
Up near the Gangotri Glacier, a genial Hindu holy man who goes by the name Mouni Baba and spends much of his life in silent meditation sees all of mankind reflected in the river.
"Human existence is like this ice," he said. "It melts and becomes water and then merges into a stream. The stream goes into a tributary which flows into a river and then it all ends up in an ocean. Some [rivers] remain pure while others collect dirt along the way. Some [people] help mankind and some become the cause of its devastation."
Advertisement